WHAT IS LASSA FEVER ?
Lassa fever is an acute viral illness that occurs in West Africa. The illness was discovered in 1969 when two missionary nurses died in Nigeria. The cause of the illness was found to be Lassa virus, named after the town in Nigeria where the first cases originated.
Lassa fever is known to be endemic (that is constantly present) in Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone and parts of Nigeria. The number of Lassa virus infections per year in West Africa is between 300000 to 500000 cases with about 5000 deaths
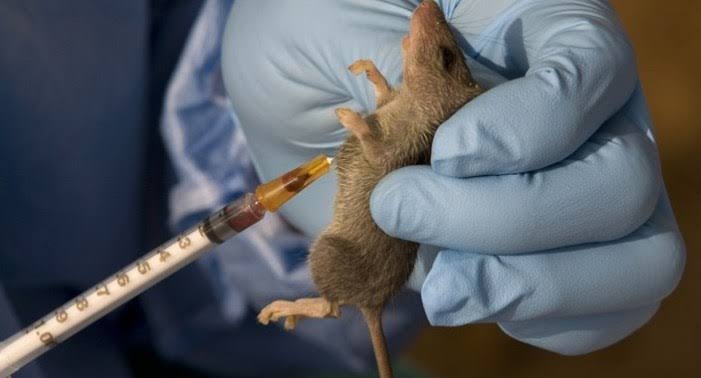
Lassa fever is a Zoonotic disease (human become infected from contact with infected animals). The host is a rodent commonly known as the “multimammate rat”. Rats infected with Lassa virus do not become ill, but they can shed the virus in their excreta (urine and feaces).
Lassa fever occurs in all age group and in both men and women. Persons at greater risk are:-
(a) Those living in rural areas where rodents are usually found.
(b) Those living in areas of poor sanitation or crowded living condition
(c) Health care workers.
How do human get Lassa Fever?
- Human usually becomes infected with Lassa virus from direct exposure to excreta of infected rats (touching the excreta) and also person-to-person transmission occurs through direct contact with the blood, urine, feaces or other body fluids of a person with Lassa fever.
- Sexual transmission of Lassa virus has been reported.
- Contact with the virus also can occur when a person inhales air contaminated with rodent excretions.
What are the symptoms of Lassa fever?
About 80% of human infected with the virus do not have any symptoms. The remaining cases have multi-system disease where the virus affects several organs in the body such as the Liver, Spleen and Kidneys.
usually gradual starting with fever and weakness. After few days, headache, sore throat, muscle pain, chest pain, vomiting, diarrhea, cough and abdominal pain may follow.
Severe cases may progress to facial swelling, fluid in the lungs, bleeding from nose, mouth, vagina and low blood pressure, Shock, seizures, tremor, disorientation and coma may be seen in later stages.
How is the disease diagnosed?
Because the symptoms of Lassa fever are so varied and non – specific, clinical diagnosis is difficult. It is difficult to distinguish from many other diseases which cause fever including malaria, typhoid fever and yellow fever.
Definitive diagnosis requires testing that is available only in highly specialized laboratory.
How is Lassa Fever treated?
RIBAVIRIN an antiviral drug is effective if given early in the course of the illness.
How is Lassa Fever prevented?
- Promotion of good “community hygiene” to discourage rodents from entering homes and reduce its population.
- Storing grain and food stuffs in rodent proof containers.
- Disposing of garbage far from home
- Maintain clean households and keep cats
Because rodents are so abundant, It is not possible to completely eliminate them from the environment.
Family members and health care workers should always be careful to avoid contact with blood or body fluids while caring for sick persons to prevent person-person transmission of Lassa Fever.